4B - Cumberland Gap
Click on maps below to view larger individual images

|
|
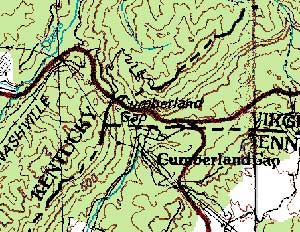
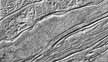
Cumberland Gap |
(Topo Map) |
||

|
|
|

|
|
|
Rationale:
The Cumberland Gap Study Area provides a classic example of how geology has influenced modern land use as well as the historical patterns of human expansion. The Cumberland Escarpment marks the topographic boundary of the Appalachian Plateaus region, but also serves to divide the highly populated farming country of the Valley and Ridge Region from the wilder, more rugged lands of the Cumberland Plateau.
Cumberland Gap technically refers only to a 1,600 foot deep notch through the Cumberland Mountain ridge, but the surrounding area boasts many other noteworthy topographic features such as fault-controlled valleys, linear outcroppings of resistant rock layers, and possible meteorite impact structures associated with the Middlesboro Basin. The ‘Gap’ was one of the few places where westward traveling pioneers could easily ascend to the heights of the plateau, following the path of Daniel Boone’s Wilderness Road, to reach westward flowing rivers leading to the fertile valleys of Kentucky. Travelers still pour through the gap today, but the main road now passes underneath the mountain, through a tunnel. The National Park Service is reclaiming the old highway route to restore the Wilderness Road to its original condition.
Themes
|
Content Outline
|
Activity TitlesAll activities include
|

|

