Various Engine Sensors and Their Locations
by Harish Kohli, Clemson Automotive Engineering Graduate Student
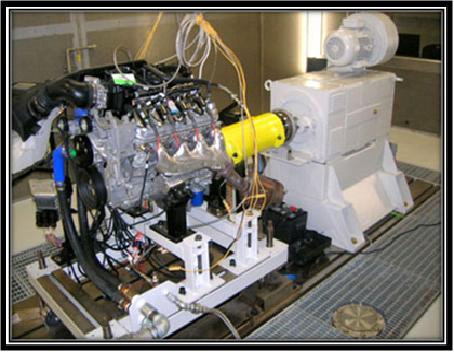
Internal Combustion Engines today are equipped with a large number of electronic sensors. These sensors keep the track of everything from the intake of air for combustion to the exhaust gas emissions. Electronic systems help engines to deliver excellent performance with good fuel economy and reduced levels of harmful emissions.
The images below show the locations of different electronic sensors on a GM 5.3L V8 VORTEC Engine. This engine is show on the right located in the Engine Dyno Test Cell at the Clemson University International Center for Automotive Research.
Sensors identified below are the:
- MAF(Mass Air Flow) Sensor
- Temperature Sensor in the combustion chamber
- Engine Knock Sensor
- Engine Crankshaft Position Sensor
- Temperature Sensor/Mid catalytic on the Catalytic Converter
- Oxygen Sensor on the Catalytic Converter
- Exhaust Air Temperature Sensor
- Throttle Position Sensor
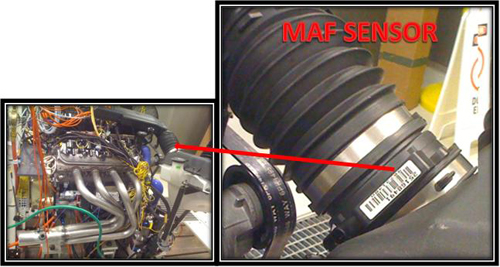
Mass Air Flow Sensor
The mass airflow (MAF) sensor is a sensor that is used to measure the volume of air entering into the combustion chamber through the intake manifold. Air expands and contracts with changes in temperature and pressure, so it is very important to mass of the air entering the combustion chamber rather than the volume in order to get the correct ratio of air and fuel for proper and well timed ignition. The MAF sensor provides this information to the ECM (Engine Control Module).
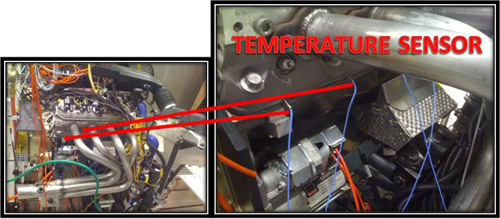
Combustion Chamber Temperature Sensor
A temperature sensor is located in the combustion chamber of each individual cylinder. These expensive sensors are used for research purposes only.
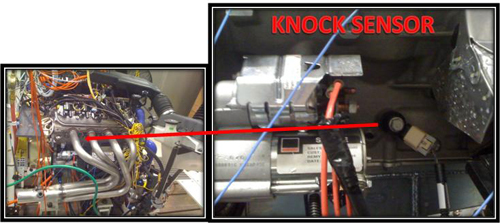
Engine Knock Sensor
The engine knock sensor measures or detects the vibrations that may result from incomplete combustion of the fuel inside the combustion chamber. When these vibrations are detected, the ECM retards the ignition timing slightly to prevent damage to the engine.
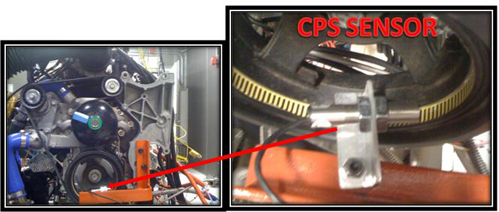
Engine Crankshaft Position Sensor
The crankshaft position sensor is used to determine the position of the crankshaft and the first cylinder. Data from this sensor is used to determine that how fast the engine is running. Also, with the help of this sensor proper firing order is maintained controlling the ignition timing and the operation of the fuel injectors.
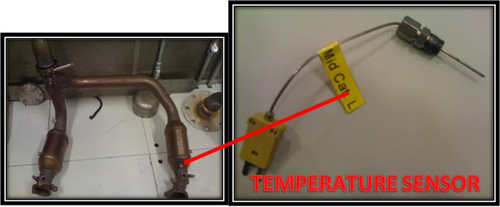
Catalytic Converter Temperature Sensor
A temperature sensor on the catalytic converter is used to measure the temperature of the gases which are entering the catalytic converter. Reactions which are taking place inside the catalytic converter are sometimes endothermic and sometimes exothermic. So we want to measure the temperature change of the gases taking place in the middle of catalytic converter and for that we use Mid-Catalytic Temperature Sensor.
Oxygen Sensor on the Catalytic Converter
The catalytic converter helps to reduce the harmful carbon and nitrous content in the exhaust gases of internal combustion engines. Oxygen sensors are used to determine the amount of oxygen in the exhaust gas. This information is used by the engine controller to make the necessary combustion adjustments to minimize harmful emissions and protect the catalytic converter from overheating.

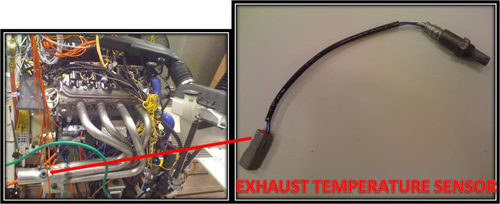
Exhaust Gas Temperature Sensor
The exhaust gas temperature sensor measures the temperature of exhaust gasses.
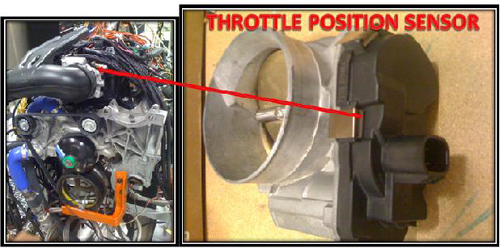
Throttle Position Sensor
The throttle position sensor is located on the throttle body and is used to determine the position of the throttle's butterfly valve. The sensor resistance changes depending upon the position of the valve. There are generally two redundant sensors located in the same housing.
|









