Wireless Charging Of Electric Vehicles
by Bharat Bhanukumaran, Clemson Automotive Engineering Graduate Student
-
The rise in the popularity of electric cars has always been dampened by the long recharging cycles they require. Public electric recharging points and battery swapping stations are a couple of measures that have been implemented to assist electric car owners who want to go on long drives. However these measures are largely dependent on the level of demand. A isolated charging station in the middle of a busy road will see hundreds of people queuing up if every passing electric vehicle has to charge there to complete their trip. To solve the problem of having to stop the vehicle for long durations, the use of wireless charging systems has been suggested.
- Methods Of Transferring Electricity Wirelessly
-
- Inductive coupling
- Magnetically coupled resonance
- Radio frequency transmission
- Laser transmission
Radio frequency transmission
This wireless electricity technology utilizes a transmitter to transmit power in the radio frequency to be picked up by a receiver at distances as far as 85 feet. The receiver converts the radio waves into current which can then be utilized for any purpose. Radio frequency transmission cannot be used to transmit power at levels required for use in vehicles. The cost to implement a radio frequency system would outweigh the returns.
Laser transmission
Laser diodes are used to beam optical energy to photovoltaic cells , which can convert them into electricity. While the laser transmission system can transfer enough energy , it would not be feasible to use this system as the laser needs to be oriented in the direction of the photovoltaic cell, which would be on the moving vehicle, to transfer power.
Inductive coupling
This contactless method of charging the vehicle is based on Maxwells Electromagnetic Laws , whereby electric current can be induced in a coil (secondary coil) when it is in the presence of a varying magnetic field. The varying magnetic field can be produced by passing alternating current through another coil (primary coil).The amount of energy induced in the secondary coil is a function of the number of coils in the primary and secondary coils and also the distance between the coils. The primary coil is laid in the asphalt of the road while the secondary coil is fixed to the underbody of the vehicle. As the vehicle passes over a section of the road with the primary coil , electricity is induced in the secondary coil which will be stored in the battery of the car.
Magnetically coupled resonance
Through magnetic resonance, two bodies with nearly the same natural frequency can exchange energy through varying magnetic fields. The necessity that the two bodies have nearly the same natural frequency is so that the transfer of energy will be done at their resonant frequency. The implication of this system in the transfer of wireless energy is to increase transfer efficiency over a varying distance between the secondary coil and the primary coil. The coils on the road and the secondary coil on the vehicle would have to have nearly the same natural frequency. Then the power can be transferred over large distances efficiently at resonant frequency.This solves the problems arising from the necessity of maintaining a constant distance between the coils in the normal electromagnetic induction process. This system can transmit at the kilowatt range.
- Requirements
-
The requirements to set up the system are categorized into the primary requirements and the secondary requirements. The primary requirement lists the most essential systems that need to be put into place to have the system functioning in its most basic form. The secondary requirement lists the necessary systems that should be put into place to ensure a fail-safe system relying on green energy.
-
Primary requirements
- Install primary charge coils in the asphalt
- Retrofit the secondary coil on the underside ( floor pan) of the car and integrate it with the battery
- Install a control system to detect when the car is moving over an inductive loop. This system should also be able to calculate the amount of electricity being used so that a bill can be drawn up
-
Secondary requirements
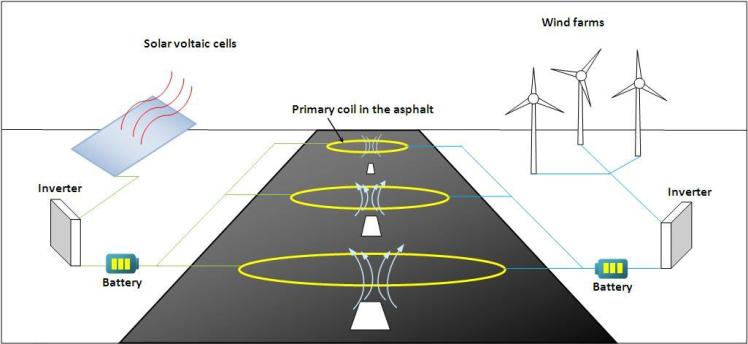
- Install solar voltaic cells/wind farms etc to charge the battery which will pass electricity through the primary coils
- Install inverters to supply AC power from DC sources like solar panels.
- Implementation Of The System
-
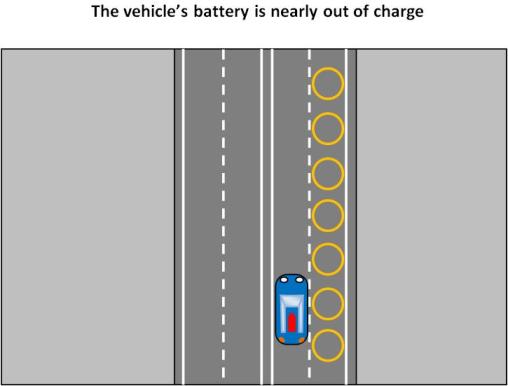
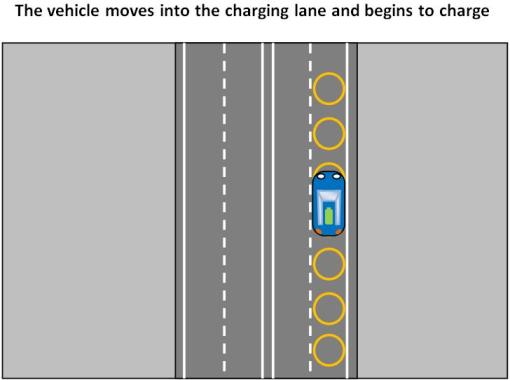
One of the suggested strategies for the implementation of the system is maintaining a charging lane on the road so that when vehicles are close to running out of charge they can shift into the charging lane where they can recharge while moving.
-
- A Reliable And Efficient Grid
-
The standard grid consists of a vast number of energy sources which are connected in not a very efficient way. A fault in the grid would affect the power supply to the cars on the road and could leave many cars stranded on the road. The solution would be to switch to a separate inclusive grid. The system would include a photovoltaic array system, inverters, and a battery (to store the charge ). The battery would supply the electricity for the primary coil.
- For More Information
- [1] Interstate Highway System 2.0, YouTube, Nov. 2009.
- [2] Students of the Karlsruhe University of Applied Sciences design electric car with wireless energy transmission, Hochschule Karlsruhe Technik und Wirtschaft website, July 26, 2010.
- [3] Drawing power from the road, Gizmag.com, October 1, 2009.
- [4] WiTricity Technology: The Basics, WiTricity.com.
- [5] Wireless Energy, New York Times, December 9, 2007.
|

