Hybrid Transit Buses
by Papeeha Thombare, Clemson Automotive Engineering Graduate Student
- Basic Description
-
Hybrid Bus technology is similar to that used in hybrid cars and trucks. It combines a conventional internal conbustion engine propulsion system with a battery propulsion system to power the vehicle.The hybrid system allows the internal combustion engine to operate in a more efficient mode, by "sharing" the energy and power demands of vehicle operations between the batteries and engine.The batteries can provide the traction motor with extra power as needed for acceleration, allowing the engine to operate with higher efficiency.The electric motor and energy storage also allows for energy recovery through regenerative braking. Regenerative braking allows the propulsion system to apply a retarding load on the drive axle during braking, thus converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy. The vehicle stores that energy in the batteries to be used as required to provide tractive effort.Transit buses are best suited for hybrid application as they have low speeds, limited acceleration and operate with frequent start and stops.There are two major ways in which the internal combustion engine can be combined with battery system :series system and parallel systems.
Parallel Hybrid System:
In parallel hybrid system an internal combustion engine and an electric motor are used for propulsion. Both of have direct, independent connections to the transmission. Either power source or both of them together can be used to power the vehicle.In addition to supplying power to the vehicle the drive motor also acts as generator and stores the surplus powersupplied to the wheels in the battery.The combustion engine provides most power at high and constant speeds while the electric motor power at low speeds and both power sources work together during accelerations.
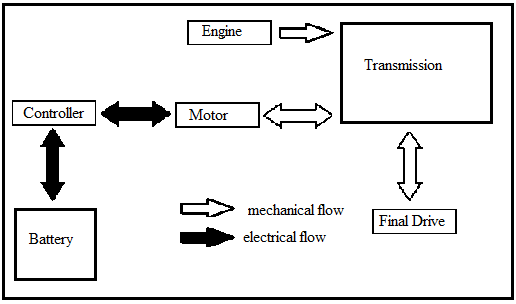
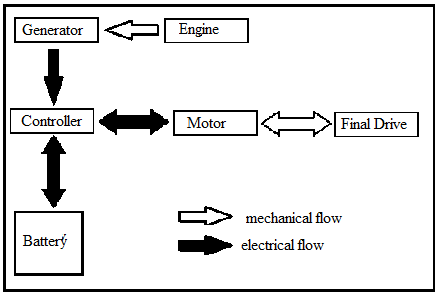
Series Hybrid system:
A series hybrid system uses an internal combustion engine to power an electric generator, which can then power the electric motor to drive the wheels, or charge the battery pack. The engine is mechanically decoupled from the drive wheels.The electric motor system by itself provides torque to the wheels.The electric motor is capable of a wide range of speeds.Because the internal combustion engine is not directly connected to the wheels, it can operate in an optimum range.The system works well in frequent stop-and-go service because the electrically-driven propulsion system has high torque at low speeds, providing smooth, fast acceleration regardless of the grade.
Advantages of hybrid trasnsit buses:
- 1) Reduced fuel consumption by 40%.
- 2) Reduced noise level due to lower RPMs.
- 3) Extended brake life due to regenerative braking.
- 4) Reduced maintenance (less engine wear and tear)
- 5) Better acceleration from a stop.
- 6 Reduced emissions
Disadvantages of hybrid transit buses:
1) The capital cost for hybrid buses is 50% to 70% more than comparable diesel buses, depending on the options ordered and the order size.
- 2) Battery life has a significant cost and operational factor.The batteries require replacement after the bus completes certain number of miles.Higher the milieage,less is the service life.The replacement is expensive as the costs of Lithium ion batteries and nickel metal hydride batteries are high.
- Sensors
- Brake pedal position, vehicle speed, energy storage (e.g. battery) status
- Actuators
- Brakes, energy storage device (e.g. battery)
- Data Communications
- Control Unit Communication: Typically Control Area Network (CAN) Bus System
- Manufacturers
- Proterra.Inc, Allision Transmission, Volvo Buses, BAE systems, ISE Cooperations, Daimler Buses
- For More Information
- [1] Hybrid electric buses, Wikipedia.
- [2] metro transit buses,YouTube.
- [3] Hybrid Buses - Allison Electric Drive System, YouTube, Jan. 28, 2008.
- [4] Hybridcenter.org,hybrid transit buses
- [5] Design studies of series hybrid transit bus ,(pdf)
- [6] Hybrid buses,Transport Canada.
- [7] Hybrid Buses: Costs and Benefits, EESI website (pdf).
- [8] Inside EPA - Hydraulic Hybrid , YouTube, May 19, 2011.
- [9] Volvo Hybrid Buses, YouTube, June 27, 2011.
|

