Regenerative shock absorbers recapture the vehicle's vibrational energy and convert it into electric energy. These actuators are still in the development stage and have not been implemented in production vehicles.
There are three kinds regenerative shock absorbers:
Piezoelectric Regenerative Shock Absorber - Piezoelectric material is used to convert the pressure to generate the necessary voltage. This method was experimented with years ago, but proved to be inefficient.
Hydraulic Regenerative Shock Absorber - Hydraulic pistons are employed to force a pressurized fluid through a turbine coupled to a generator. The damping is actively optimized by a controller, which also ensures a smoother ride compared to a regular suspension.
Electromagnetic Regenerative Shock Absorber - This shock absorber uses a stack of permanent magnets and coils forming a generator to produce electricity through electromagnetic induction. This system has advantages over the other two. First, there is no heat generation due to friction. Second, it can capture energy both during expansion or compression of the shock absorber. Finally, implementation of this kind of shock absorber does not require any major design change in the vehicle.
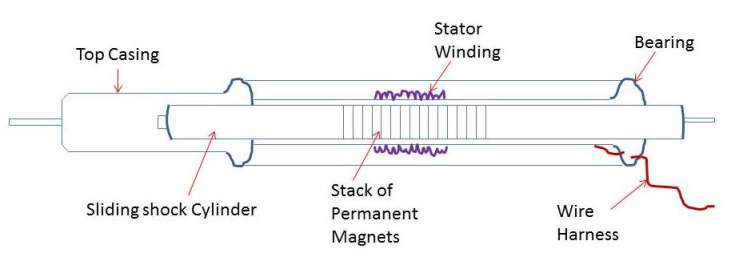
Electromagnetic regenerative shock absorbers can be of 2 kinds. Linear absorbers utilize the relative linear motion between the magnetic field and coils to generate power. Rotary absorbers convert the linear motion to a rotary motion in order to drive a generator. Rotary absorbers tend to be more efficient, but are generally more expensive to manufacturer.
German autoparts maker ZF has teamed up with the American company, Levant Power, to develop an active suspension system utilizing regenerative shock absorbers that is expected to be in production by the end of 2015.

