Gauges and Meters
- Basic Description
-
The driver of an automobile relies on various gauges and meters to get information about the vehicle's speed and general operating status. There are two types of gauges: analog and digital. Analog gauges display quantities as a needle position, bar height, or other smoothly varying indicator. Digital gauges provide numerical readouts of the quantity being measured.
Until recently, most of the gauges in automobiles were analog electric meters. The higher the applied voltage, the more the needle position changed from its rest position. These gauges employed a spring, a coil and a permanent magnet. Current flowing through the coil created a magnetic field that drew the coil towards the magnet. When there was no current, the spring returned the coil and the attached needle to their original positions. Another type of analog gauge worked by heating a bimetallic strip that bent to change the needle position. This type of gauge had a relatively slow response time was commonly used for displaying fuel levels and other applications where short-term oscillations in the measured level needed to be filtered out.
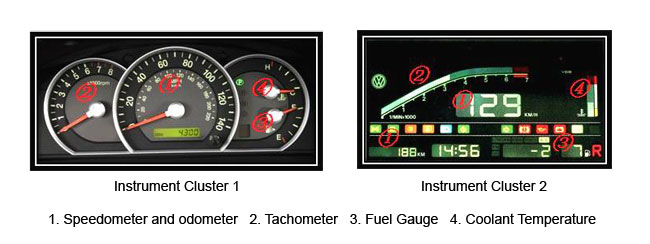
Within the past several years, stepper motors have largely replaced the analog gauges in automobiles. The stepper motor rotates or raises a needle to whatever position the digital controller has determined it should be in. Digital gauges usually employ LCD or LED displays. Most of the gauges in an automobile are found in the dashboard in front of the driver; however head-up displays (HUDs) are becoming more popular. Head-up displays usually supplement, but do not replace the gauges in the dashboard. A few of the more common gauges found in automobiles are described below:
- Speedometer - Displays the vehicle speed in miles per hour and/or kilometers per hour
- Odometer - Displays the miles the vehicle has traveled
- Tachometer - Displays the engine speed in revolutions per minute (RPM)
- Fuel Gauge - Displays amount of fuel remaining as a percentage of a full tank
- Temperature Gauge - Displays the temperature of the engine coolant
- Ammeter - Displays the amount of current being drawn from the battery
- Voltmeter - Displays the battery voltage.
In recent years, there has been a trend towards replacing all gauges in the dashboard with LCD or OLED displays. These displays have the advantage that the size, shape and color of the gauges can be changed to fit the driving situation. They also allow the dashboard to be customized for different vehicle models or even for different drivers.
- Manufacturers
-
Autogauge,
Autometer,
Classic Instruments,
Defi
- For More Information
- [1] Dashboard,
Wikipedia.
- [2] Lexus LFA Digital Speedometer, YouTube, Jan. 28, 2010.
- [3] Sharp Develops In-Car LCD with 1500:1 Contrast Ratio
, Engadget.com, 2006.
- [4] Nissan 2008 GTR - Operate Multi Function Meter, YouTube, Dec. 7, 2007.
- [5] 2011 Toyota Sienna Gauges And Meters How To by Toyota City, YouTube, Sep. 13, 2011.
- [6] How Much Current Do My Auto Meter Gauges Draw?, YouTube, Oct. 1, 2010.
- [7] Pocket-Lint Kia GT Concept T-OLED display, YouTube, Sep. 16, 2011.
- [8] How Fuel Gauges Work,
Karim Nice, HowStuffWorks.com, Feb. 9, 2021.
|

