Servo Motors vs. Stepper Motors
- Basic Description
-
Although both stepper motors and servo-motors allow for rotor position control,
they are two very different mechanisms.
Technically a servo-motor is any type of motor (AC/DC/stepper) with a closed loop controller.
A stepper motor operates without feedback, controlling the rotor’s position by rotating a set number of degrees for each input pulse.
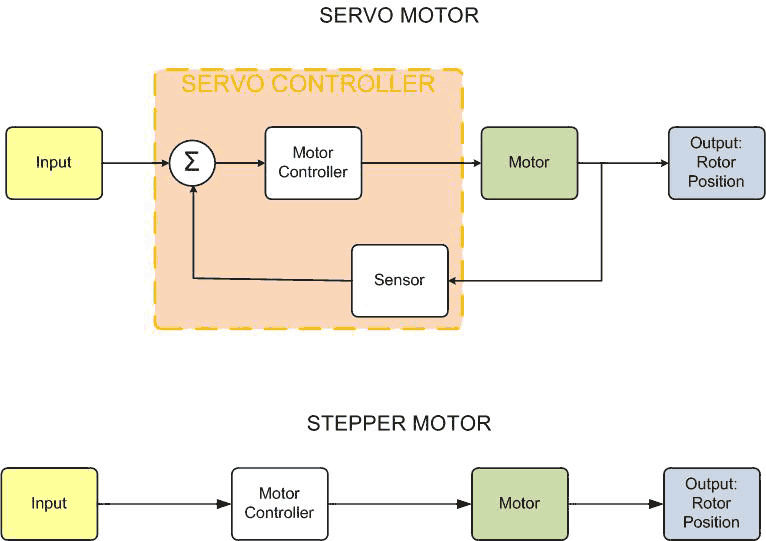
The feedback to a servo-motor is usually in the form of a position sensor or rotary encoder
attached to the motor’s rotor. The rotary encoder converts the angular position of the rotor relative to the stator into an electrical signal that is fed back to the motor controller. The motor controller then uses this information to
precisely position the rotor.
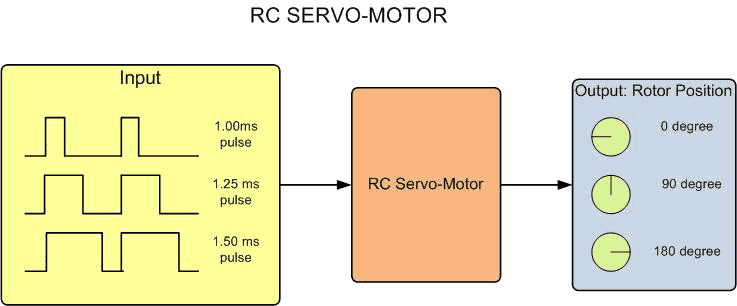
The most common type of servo-motor is an RC servo which employs a DC motor,
reduction gear, and servo controller, all within the motor housing. They are controlled using
PWM where the length of the pulse dictates how far the rotor rotates. This type of motor is
commonly used to precisely actuate mechanical components on radio-controlled (RC) models or robotics.
- Manufacturers of Servo Motors
-
Advanced Motion Controls,
Applied Motion Products,
Baldor,
Powertec,
Tamagawa Seiki,
Teknic
- Manufacturers of RC Servo Motors
-
Futaba,
GWS,
HiTEC
- For More Information
- [1] Servomechanism, Wikipedia.
- [2] How do servos work?, YouTube Video, Bartsli Polish Contributor, Sept. 25, 2008.
- [3] Hobby Servo Fundamentals, Darren Sawicz.
- [4] What is a Servo, Seattle Robotics Society, non-profit org.
- [5] Servo vs. Stepper Motors, engineeringpost.com.
|

