Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
- Basic Description
-
Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS) are mandatory
on all new cars sold in the United States since 2007 and all cars sold in Europe since 2012.
Tire pressure monitoring systems monitor the internal temperature
and pressure of an automobile's tire. These systems warn drivers
of under inflation, leaks, and the loss of air pressure that occurs
naturally. Tires typically lose about 1 psi (pounds per square inch)
each month due to natural permeation. This loss can be greater in warm
weather.
In an under-inflated tire the sidewalls will flex
excessively creating high temperatures that degrade the tire and make
failure more likely. The chief challenge to measuring tire pressure is
the simple fact that the tire is rotating at high speeds and making a
direct electrical connection to a rotating tire is difficult.
The tire is also exposed to unexpected hazards, water, and road
chemicals and subjected to severe centrifugal forces. TPM systems
must be designed to endure these harsh conditions and meet four key
requirements: They must secure the sensor in the tire or wheel, provide
power to the sensor, extract data from the sensor, and display the
information to the driver.
-
-
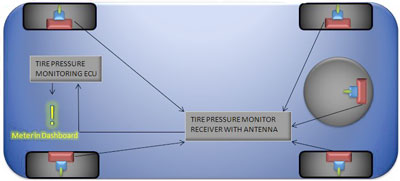
Direct Systems attach a pressure sensor/transmitter
to the vehicle's wheel inside the tire's air chamber.
An in-car receiver warns the driver instantly if
the pressure in any one tire falls below a predetermined level.
Indirect Systems use the vehicle's antilock braking
system's wheel speed sensors to compare the rotational speed of one
tire vs. the others. If one tire is low on pressure,
it will turn a different number of revolutions per mile than the
other three tires. Newer systems, also collect information from the electronic stability control system and/or other systems and are capable of detecting pressure drops in one, two, three or even all four tires.
Some of the newer TPMS systems assist with the process of inflating a tire by briefly sounding the horn and/or flashing lights when a tire reaches the correct inflation pressure.
- Sensors
- Air pressure sensor, temperature sensor, wheel speed sensor
- Actuators
- Low-tire-pressure display
- Data Communications
- Data communication between tires and control unit:
typically 315 MHz RF link.
Wake-up signal to tire mounted sensors: typically a
low-frequency EM signal.
Control unit communications: typically CAN bus
- Manufacturers
-
Bartec,
Continental,
Doran,
Dorman,
Huf,
Johnson Controls, NIRA Dynamics,
Pressure Pro,
Schrader,
Sigma Automotive,
SmarTire,
TRW,
VisiTyre
- For More Information
- [1] Transportation Recall Enhancement, Accountability, and Documentation (TREAD) Act,
Section 12, "Tire pressure warning."
- [2] Tire-Pressure Monitoring System, Wikipedia.
- [3] Toyota Prius TPMS Tire Pressure Monitoring System, YouTube, Nov. 2008.
- [4]
Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) at Freescale Ford Road Show, YouTube, Mar. 2009.
- [5]
Johnson Controls' Advanced Tire Pressure Monitoring System, YouTube, Apr. 20, 2010.
- [6]
2012 NISSAN Altima - Tire Pressure Monitoring System, YouTube, Sep.23, 2011.
- [7]
Pep Boys Explains TPMS -Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems Video, YouTube, June 1, 2012.
- [8]
2013 Nissan LEAF - Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS), YouTube, Mar. 7, 2013.
- [9] What is TPMS & How Does it Work?, Bridgestone Tire website, April 28, 2014.
- [10] 2015 Nissan LEAF - Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS) with Easy Fill Tire Alert , YouTube, June 27, 2014.
|

