Four Wheel Steering
by Mathew Angayil, Clemson Automotive Engineering Graduate Student
- Basic Description
Four Wheel Steering or All Wheel Steering (AWS) is a system available in a growing number of vehicles that can improve driving characteristics and safety. Early implementations of four wheel steering were limited to a constant level of maneuverability due to the limitations of hydraulic power steering (HPS). Electronic Power Steering (EPS) systems increase the level of control available and make AWS a much more appealing option.
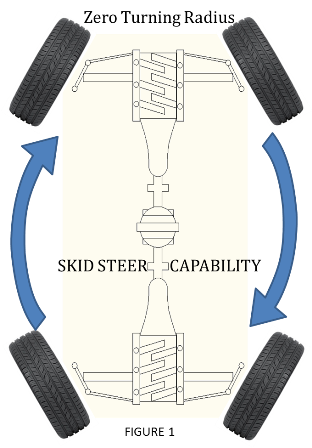
Four wheel steering systems steer the vehicle by turning all four wheels. Most systems can turn the front and rear wheels independently. Some systems can turn all four wheels at different angles like the one shown in figure 1. This mechanism allows the vehicle to have a near-zero turning radius or skid steer capability.
How the system works:
- The same EPS module found in cars with two-wheel steering is used to turn the wheels in the front based on the inputs from various systems like the vehicle speed, ABS, ESP, yaw rate etc.
- The rear wheels work on sensors and actuators independent of the front wheels. The rear wheels are limited from turning as far as the front wheels.
- A control unit decides the turning angle of the rear wheels. It takes input from all those sensors related to normal steering and stability programs.
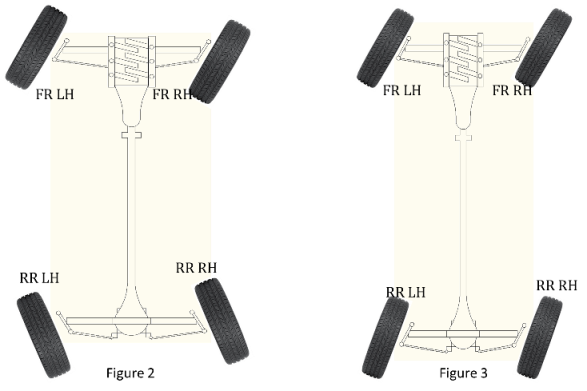
- At lower speeds, the rear wheel turn in the opposite direction from the front wheels as shown in Figure 2. This will help in easy maneuverability of the vehicle during parking and taking a tight curve. The turning radius of a vehicle can be reduced by a minimum of 20% by having this mechanism, which is a significant benefit for bigger cars and trucks.
- At higher speeds, the rear wheels turn in the same direction of the front wheels l(Figure 3) to increase stability by preventing oversteer and fish tailing.
Four wheel steering has 4 major benefits. One is to reduce the steering angle therefore increase safety by reducing the required response time. It also improves the ease of maneuvering during tight corners or parking. It helps to increase the stability at higher speeds and also helps to make quicker lane changes even if the vehicle is towing. Advanced four wheel steering systems are capable of turning the rear wheels in opposing directions, which can help in difficult braking conditions.
- Advantages
- Provides additional active safety options
- Improves steering response
- Higher vehicle stability at higher speeds
- Higher maneuverability at lower speeds
- Decreased turning radius
- Improves lane changing and reduces snaking effect while towing.
- Sensors
- Steering wheel torque sensor, steering wheel position sensor, wheel speed sensor, Yaw Rate sensor
- Actuators
- Electric motor
- Data Communications
- CAN bus data communication between ESP and engine controller
- Manufacturers
- Delphi
- For More Information
- [1] Renault Laguna GT Animation, YouTube, June 2, 2008.
- [2] Four Wheel Steering, Wikipedia.
- [3] Quadrasteer, Delphi flyer. (pdf)
- [4] Renault Laguna at Lower speeds, YouTube, Apr. 1, 2008.
- [5] Four Wheel steering, Ease of maneuverability, YouTube, Mar. 31, 2008.
- [6] Four Wheel Steering Explained, www.gizmag.com.
- [7] Four Wheel Steering, Infinity, YouTube, July 7, 2010.
|

