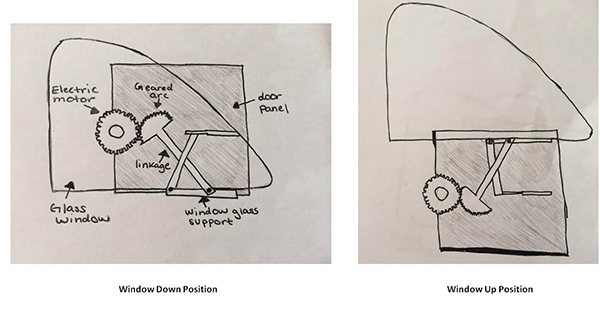
The first power windows were introduced in cars in 1940 by Packard using a hydro-electric system, and since the 1970's the operational design has not changed significantly. In a basic system, power is run to the motor as switches are activated based on the user input. In some cars though, the power does not go through the switches directly and instead connects to a microcontroller which monitors the state of the switches and if the switch status is changed, the microcontroller closes a relay to provide power to the window motor. The driver is able to control other windows by sending data on a communication bus to tell the controller to open/close other windows. Most power window systems consist of 4 basic components: the battery, a switch, a motor, and gears. The gears are connected to linkages that attach to the bottom of the window.
The window follows a track in the door to allow for smooth operation of the window's motion. The DC motor works in a 2 to 5 amp current range and is controlled through a relay. The basic motor operation is accomplished by reversing the polarity of the motor to make the window move up or down. The motor is able to tell when the window is closed by using a thermal sensor. The motor lifts the window until the glass is fully up, when this happens the motor will still be trying to push the window up, but the glass has no where to go so it creates resistance and heat in the motor. The sensor detects the change and turns the motor off.
On cars today, there are three types of switches. Rocker switches, toggle switches, and lever or push-down/pull-up switches. There has been scrutiny over the safety of power windows as several deaths have occurred from children's arms or necks becoming trapped by an accidentally triggered window. To prevent these accidents, car manufacturers have implemented a driver-controlled lockout switch to prevent other passengers from using the switch as a toy or allowing the switch to accidentally be activated while a child or pets head is out the window. Lever switches are considered to be the safest design for power windows, so since Oct. 1, 2010 the government has required that all new passenger vehicles with power windows be equipped with lever switches. Rocker and toggle switches can be accidentally activated by downward pressure on the switch, but, with lever switches, the windows cannot be closed due to unintentional pressure. Windows can also be designed for safety by implementing automatic-reverse power windows which monitor the window speed, and if the speed is slowed (by an object in the way of the window's motion) then the circuit reverses power and begins to go back down so that it does not close with a child or arm in the way of the window's motion. Many child safety advocates support making the automatic-reverse windows mandatory, but the NHTSA announced that they would not pursue this regulation because many of the fatal injuries involving power windows had already been addressed with the requirement of lever switches.
Features of Power Windows:
Automatic up/down: A common feature that monitors the amount of time you hold the switch down. If the switch is held for less than about half a second then the window will go down all the way until it reaches its limit. If the switch is held for longer then it will stop motion when the switch is released.
Courtesy power on: Generally, as a security feature, power windows are usually inoperable when the car is not running, but sometimes a small amount of power is needed to roll up the windows when the car has just been turned off. This courtesy power on feature is seen on most cars today and maintains a small amount of power to the window circuit after the car is turned off to allow you to roll up the windows. The power window has a relay that will provide power to the circuit. Some cars keep this relay closed for up to a minute, while other car manufacturers provide power available to the window motors until a door has been opened.
Window control from the outside: Volkswagen has introduced a feature in which the windows can be lowered by inserting a key in the driver's door, turning and holding it. The door module monitors a switch in the door lock and if the key is held and turned for more than a set amount of time, the driver's door module lowers the window.

