- ... 1).1
-
In general, a point in an n-dimensional Euclidean space is
represented as a point in an (n+1)-dimensional projective space.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ... ``line''2
-
Since it can become confusing to read statements such as,
``A point is represented as a `line,' '' we will always enclose
in quotation marks the entities whose sole purpose is visualization
in n+1 dimensions.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
space,3
-
Do not be confused by the term space, which can refer to either
three dimensions or an arbitrary number of dimensions.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
- ...
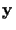 ,4
,4
-
If
![$\ensuremath{{\bf t}} =\left[\matrix{a \cr b \cr c}\right]$](img155.gif) ,
then
,
then
![$[\ensuremath{{\bf t}} ]_x = \left[\matrix{0 & -c & b \cr c & 0 & -a \cr -b & a & 0}\right]$](img156.gif) .
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
![$\ensuremath{{\bf t}} =\left[\matrix{a \cr b \cr c}\right]$](img155.gif) ,
then
,
then
![$[\ensuremath{{\bf t}} ]_x = \left[\matrix{0 & -c & b \cr c & 0 & -a \cr -b & a & 0}\right]$](img156.gif) .
.